As the end of the year approaches, employers and members of the Social Security System (SSS) in the Philippines must prepare for possible adjustments in contribution rates. This document provides a detailed overview of the current rates as mandated by the SSS. Should any modifications be announced, we will promptly update the information herein to keep all stakeholders informed.
Employer Obligations and SSS Contribution Requirements
Employers are obliged to remit contributions to the SSS on behalf of their employees. These contributions ensure employees are eligible for SSS benefits, which provide financial assistance during retirement, illness, maternity, or disability.
Historically, the SSS set deadlines for contributions based on the last digit of the employer’s or individual member’s SSS number. For 2023, contributions must be made by the last day of the month following the month for which the contribution is applicable.
Contribution Timelines
The schedule for SSS contributions is dependent on the type of membership:
- Regular Employers: Contributions are due by the last day of the month following the contribution period.
- Self-Employed Individuals: Payments must be made by the last day of the month after the quarter ends.
- Informal Sector Members (e.g., farmers, fisherfolk): Contributions can be made at any time throughout the year, providing flexibility to those in irregular employment.
SSS Contribution Rates for 2024
Employers (ER) and Employees (EE):
Employers are responsible for collecting and remitting both their own contributions and those deducted from employees’ salaries. Employees’ contributions are withheld from their salaries by their employers.
The specific rates are detailed in the tables provided below.
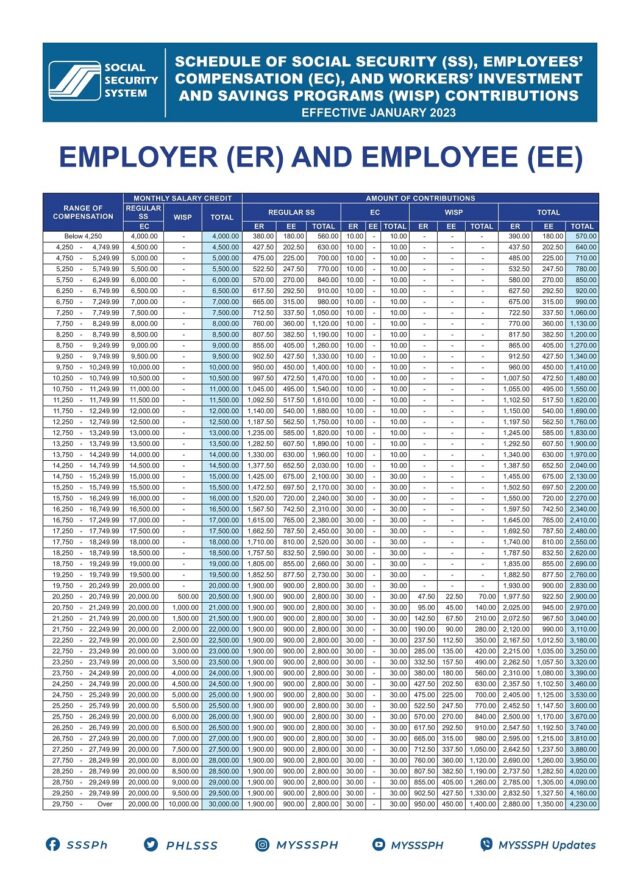
Household Employers (HR) and Kasambahays (Household Employees) (HE):
Household employers must register their kasambahays with the SSS to facilitate their contributions, which ensures kasambahays are eligible for benefits like health insurance and retirement pensions.
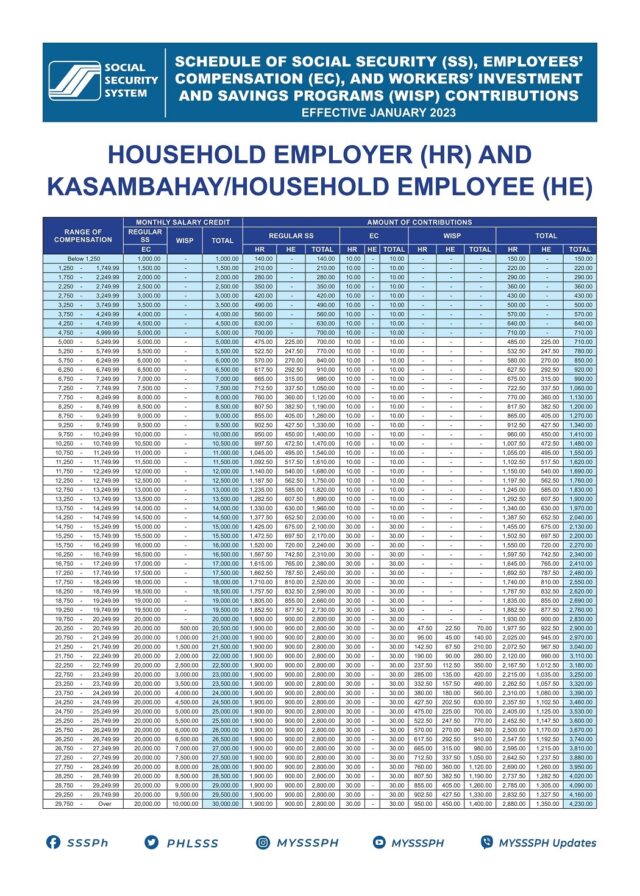
Land-based Overseas Filipino Workers (OFWs):
OFWs need to make contributions to the SSS to maintain their eligibility for benefits, which can be crucial during periods of employment abroad and upon their return to the Philippines.
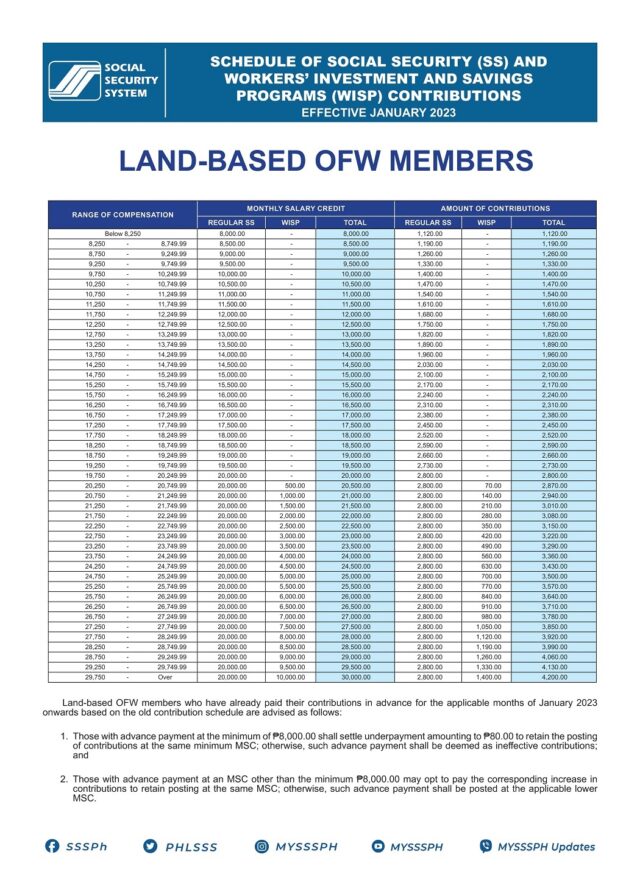
Self-Employed Members:
Individuals who operate their own businesses or work freelance are required to contribute to the SSS based on their declared earnings to gain access to SSS benefits.
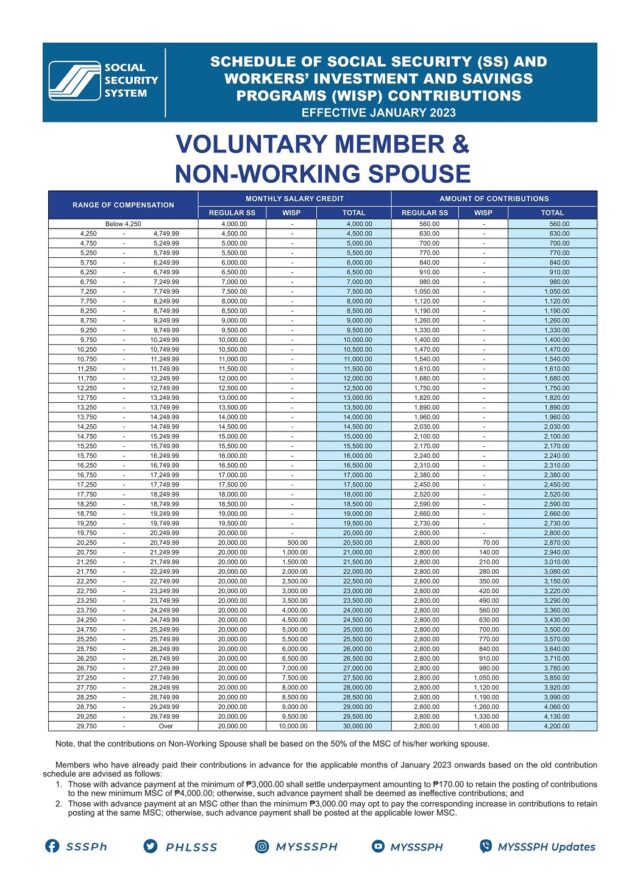
Voluntary Members and Non-Working Spouses:
Voluntary members are those who are not employed but wish to contribute to the SSS to qualify for future benefits. Non-working spouses of SSS members may register to become eligible for benefits through voluntary contributions.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Timely SSS contributions are critical. Late payments are subject to penalties, including fines and interest charges, which can complicate benefit claims and lead to possible disqualification from specific benefits. Ensuring prompt payment of SSS contributions is essential for maintaining eligibility for the comprehensive benefits offered by the system and avoiding potential financial liabilities.
Maintaining Compliance
Employers and individual members must keep accurate records and adhere to prescribed timelines to avoid penalties. Regular updates from the SSS regarding rate adjustments or policy changes should be monitored to ensure compliance and continued eligibility for benefits.

